7/27受付開始!夏休みワークショップ開催!!
2020-07-28 13:59
こんにちは!
例年であればすでに小学校の夏休みも始まっている頃ですが、今年はコロナの影響からほぼ全ての学校で夏休みが短縮されていますね。
落ち着かない日々がまだ続いていて、今年の夏は出かける予定を立てられないご家庭も多いのではないでしょうか。
さて、エデュテックスクールでは8月9日、10日、12日に夏休みのワークショップを開催することに致しました。
どこにも出かけられない子ども達に少しでも楽しい経験をしてもらえたらと思っての開催です。
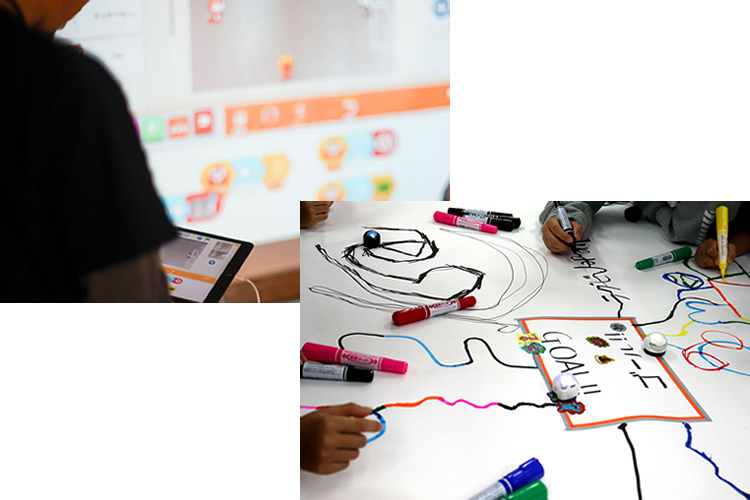
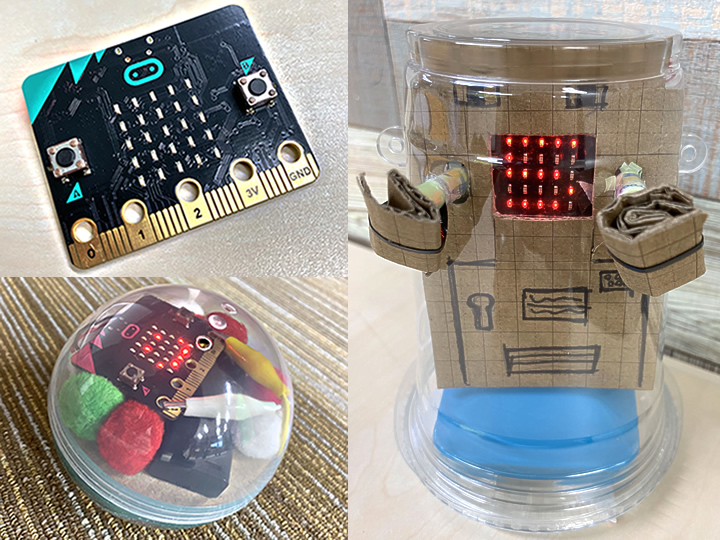
今回のワークショップでは、普段教室で使用している教材ではなく、micro:bitという教育向けのマイコンボードを使ってプログラミングと電子工作にチャレンジする事ができます。
今年は自由研究の無い小学校も多いようですが、自由研究にもそのまま使えるような内容にしていますので、予定の空いてしまったお子さまをこの機会に参加させてみてはいかがでしょうか。
もちろんプログラミング未経験でもOK!工作好きな子も大歓迎!
是非この夏の経験の一つにしてあげてください。
ワークショップの詳細はこちらの案内PDFからご確認ください。
なお、感染症予防対策のため一回の人数を限定しての受付としています。
お申し込み状況によりお席がご用意できない場合もございますが、あらかじめご了承くださいませ。
ワークショップのお申し込みはこちらから。
無料体験授業の方も引き続き受付をしております。
こちらも1回の人数を限定しての体験授業にしておりますので、ご希望の方はお早めにご予約ください!
無料体験授業のお申し込みはコチラから!
ご不明点などはお気軽にお問い合わせください!